With data entry and organization, Microsoft Excel can also perform beginner to intermediate-level data analysis easily nowadays. For our everyday use, it can provide functional tools that go a long way. Data cleaning is the primary step for any data analysis method. It includes removing, preparing, or converting unwanted or irregular values to usable ones. In this tutorial, we will discuss different data cleaning techniques and how to perform them in Microsoft Excel.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the workbook used for the demonstration from the link below.
19 Data Cleaning Techniques in Excel That Will Come in Handy
We will be discussing a total of 19 different data cleaning techniques in Excel in this article. All of them are important in different cases more or less. Follow along to see how each of them works or find the one you need from the table of contents above.
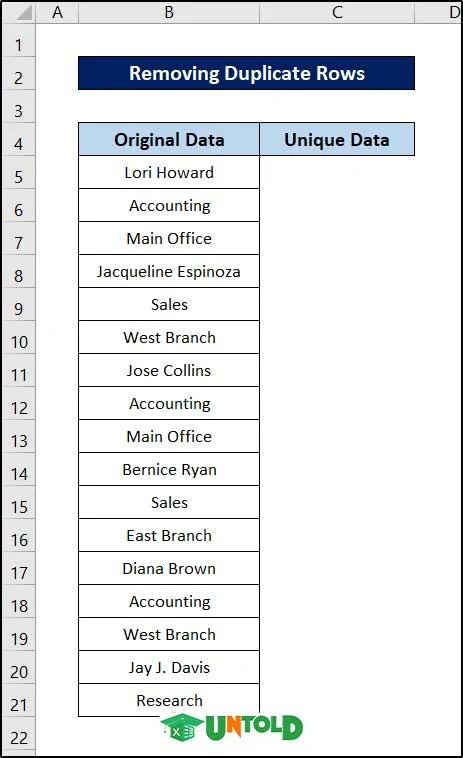
1. Remove Duplicate Rows
Your data may have duplicate rows, whatever the reasons. Most of the time, you need to eliminate duplicate rows. In old days, removing duplicate data was a manual task- although removal works could be done with advanced techniques. But with the Remove Duplicates command, removing duplication is now an easy job. Remove Duplicates command was introduced in Excel 2007.
Let’s replicate the column beside and then remove the duplicates to compare them later on.
Follow these steps to remove duplicates.
Steps:
- First, select the column you want to remove duplicate from.
- Now go to the Data tab on your ribbon.
- Then select Remove Duplicates from the Data Tools group there.
- After that, select Continue with the current selection option in the pop-up box and click on Remove Duplicates.
- Next, click on OK.
This will remove all the duplicates from the selection.
Read More: How to Clean Survey Data in Excel
2. Highlight Duplicate Values
Sometimes instead of removing the duplicate values altogether, highlighting them is helpful. Here we will show you different scenarios and methods of highlighting duplicate values.
Utilizing Conditional Formatting
In the first portion, we are going to utilize the Conditional Formatting feature to highlight duplicate values. We will do that on the following dataset.
Follow these steps to see how we can do that.
Steps:
- Firstly, select the cells that we want to duplicate. In this case, it is D5:D18.
- Secondly, go to Home > choose Conditional Formatting > go to Highlight Cells Rules > select Duplicate Values.
- Eventually, a Duplicate Values window will appear.
- Thirdly, choose Duplicate.
- Fourthly, select any color options in the values with In this case, we have selected Light Red Fill with Dark Red Text.
- Consequently, we’ll see that the duplicate values in the D Column are highlighted.
Highlighting Duplicates Including First Occurrence
Now, for the same dataset, we are going to highlight duplicate values including the first occurrence. This is the same as the previous one mentioned. But we will follow a different route here along with the COUNITF function. Follow these steps to see how this method works.
Steps:
- Firstly, go to the New Formatting Rule window by going to the Conditional Formatting
- Secondly, choose Use a formula to determine which cells to format.
- Thirdly, write the following formula in the formula box.
=COUNTIF($D$5:$E$16,$D5)>1
- Consequently, we’ll notice that the D column is highlighted for duplicates, including the 1st occurrences.
Highlighting Duplicates Excluding First Occurrence
Now we are going to discuss another one of the most useful techniques to identify duplicate values. It does not highlight them excluding the first occurrences. This is helpful if we want to observe the recurring values only instead of all the duplicate values. Just like the previous one, we will utilize the COUNTIF function here.
Follow these steps to see how we can do that.
Steps:
- To do this, first, go to the New Formatting Rule through the Conditional Formatting option as we have discussed before.
- Secondly, select Use a formula to determine which cells to format in the same way as before.
- Thirdly, write the following formula in the formula box.
=COUNTIF($D$5:$D5,$D5)>1
- After clicking on OK, it will highlight all the duplicates excluding the first occurrences.
Read More: How to Clean Up Raw Data in Excel
3. Split Text into Multiple Cells
When you import data from another source, it may happen that multiple values have been imported into a single column. The following image shows an example of this type of import incident.
There is a useful Text to Column feature that we can use that will help us split these texts.
Steps:
- First, select the range you want to split text from.
- Then go to the Data tab on your ribbon.
- After that, from the Data Tools group, select Text to Columns.
- Next, select Delimited in the next box.
- After clicking on Next, another box will appear.
- Select Space here under Delimiter options as the text is divided by spaces.
- Then click on Next.
- After that, click on Finish.
- Finally, the text will split.
- Now let’s make some modifications to make it more presentable.
This is how we can split texts into different cells along with other data cleaning techniques in Excel.
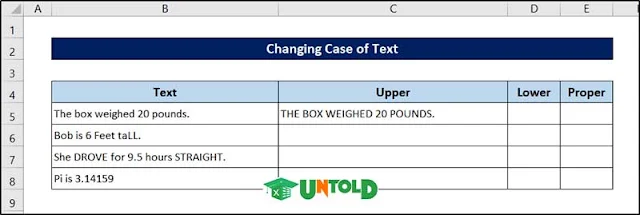
4. Transforming Data with Formulas
Sometimes, you may want that the case of your text will be the same. Excel does not provide any direct way to change the case of text, but you can do it easily using some formulas. The three formulas to change the text are:
UPPER: This formula converts the text to ALL UPPERCASE.
LOWER: This formula converts the text to all lowercase.
PROPER: This one converts the text to Proper Case (the first letter in each word will be capitalized, as in a proper name).
We will use the following dataset for all the presentations.
Changing to Upper Case
As mentioned earlier, we will use the UPPER function for this purpose. Follow these steps to see how we can do that.
Steps:
- First, select cell C5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=UPPER(B5)
- After that, press Enter.
- Now select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to fill the rest of the cells with the formula.
Changing to Lower Case
Next, we will demonstrate how to convert all of the text into lowercase.
We will follow the following steps for this.
Steps:
- First, select cell D5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=LOWER(B5)
- After that, press Enter.
- Now select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to fill the rest of the cells with the formula.
Changing to Proper Case
The proper case indicates the capital letters in proper places and lowercase in other places. For this dataset, we are using the following method for this.
Steps:
- First, select cell E5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=PROPER(B5)
- After that, press Enter.
- Finally, select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to fill out the rest of the cells.
5. Remove Extra Spaces
It is always a very important issue to ensure that the text doesn’t have extra spaces. It is not possible to find out a space character at the end of a text string. Extra spaces create lots of problems, especially when you need to compare text strings. Say for example “July” is not the same as “July “. The first one is four characters long and the second one is five characters long.
We can follow these two data cleaning techniques in Excel to remove extra spaces.
We will be using both of them in the following dataset.
Using TRIM Function
We use the TRIM function to remove all leading and trailing spaces from a text. The TRIM function also replaces multiple spaces with a single space.
Steps:
- First, add a column named Updated Data to show the results.
- Then click on Cell D5.
- Type =TRIM and select Cell C5 in the first argument. Close the parenthesis.
- So, the formula becomes:
=TRIM(C5)
- Now, press Enter.
- Now drag the Fill Handel icon to the last cell.
We can see that unnecessary spaces are removed; only single spaces exist after each word.
Using Find & Replace Feature:
In this section, we will discuss how to use the Find & Replace command to remove all spaces.
Steps:
- First, select the data from where we want to remove the extra spaces.
- Then go to the Home tab.
- From the Editing command, go to the Find & Select feature.
- Select Replace from the drop-down list.
- When we select Replace, we will get a dialog box.
- Type a blank space in the Find what field.
- Keep the Replace with box empty.
- Then, click Replace All.
- After clicking Replace All, we will get a Pop-Up showing the number of replacements.
- Now click OK on the Pop-Up.
- Then click Close of the dialog box.
- Finally, we get the result.
6. Remove Strange Characters
Often, after importing data into an Excel worksheet, you will find that there are some strange (sometimes unprintable) characters. You can use the CLEAN function to remove all non-printing characters from a text. If the data is in cell A2, you can use to do your job:
=CLEAN(A2)
The CLEAN function sometimes may miss some non-printing Unicode characters. It’s programmed to remove the first 32 non-printing characters in the 7-bit ASCII code. Browse the Excel Help system for information on how to remove the non-printing Unicode characters.
7. Convert Values
Another important one in data cleaning techniques is to convert one value in a dataset to another. Sometimes you may need to convert values from one metric system to another metric system. For example, you may import a file that has values in fluid ounces (fl oz), and they need to be expressed in milliliters. Excel’s CONVERT function can perform this type and many other types of conversions.
This function is extremely helpful and can handle the most common measurement units in the following categories: weight and mass, distance, time, pressure, force, energy, power, magnetism, temperature, volume, liquid, area, bits and bytes, and speed.
For a demonstration, let’s look at a dataset and apply this to it. This is the dataset.
Follow these steps to change the temperature to Fahrenheit.
Steps:
- First, select the output cell D5
- Then type the following formula
=CONVERT(C5,"C","F")
- After that, press Enter.
- Now click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to convert all values.
This is how we can convert values into other units. For other unit conversions, check out this article.
8. Highlight Errors
Due to a lack of proper formula or string or values, the spreadsheet will show errors. If you start searching them one by one it will take a lot of time. Below I have explained an easy technique to find errors and highlight them so that you can find them easily.
Suppose we have a dataset with some errors in some cells. Now we will highlight them with conditional formatting and the Go to Special feature of excel.
Let’s take a look at the following spreadsheet.
Follow these steps to highlight errors here.
Steps:
- Above all, select the whole dataset and click New Rule from the Conditional Formatting options.
- Then, in the rule type choose Format Only cells that contain and then select Errors from the below drop-down list.
- Then click on OK.
This is the final result of the dataset. As you can see, Excel highlighted the error values.
This is how you can highlight errors as one of the data cleaning techniques in Excel.
9. Join Columns
Joining columns is another one of those techniques we may need some time while cleaning or rearranging data. For this demonstration, let’s take the following dataset.
Follow these steps to see how we can join these texts from individual cells in Excel.
Steps:
- First, select cell E5.
- Then write down the following formula.
=B5&" "&D5&" "&C5
- After that, press Enter.
- Now click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to replicate the formula for the rest of the cells.
This is how we can join two or more columns in Excel.
10. Rearrange Columns
Sometimes you may need to rearrange the columns in a worksheet. If you think for some minutes, you can solve this problem in this way: you can create a blank column and then drag another column into the new blank column. The moving column will leave a gap and you have to delete that column after your job is done.
Here’s an easier way you can use to rearrange the column easily we are doing on the following dataset.
Steps:
- First, select the column you want to move by clicking on the column header.
- Then cut the column using either the context menu or pressing Ctrl+X. You will see the dotted line at the border of the selection at this point.
- After that, right-click on the column header before which you want to place the previous column.
- Now select Insert Cut Cells from the context menu.
- This will insert the previous column here.
This is how we can rearrange columns as part of data cleaning techniques in Excel.
11. Randomize Rows
In this section, we will be discussing randomizing rows. Although not particularly useful in most cases, it is still a handy trick if you want to rearrange a dataset. Or if you want to change the order of a list through Excel.
We are going to perform such a task for the following dataset.
Follow these steps to randomize the rows and change up the order in Excel.
Steps:
- First of all, we have to create a new column after column B. For this, click the header letter of column C, and the whole C column will be selected.
- Then, right-click and choose the Insert command, and a new column will be created.
- Now, assign a name to the newly created column (i.e. Random Number). Select the first cell (i.e. C5) column and type the following formula into the cell.
=RAND()
- After that, press ENTER, and a random number will be displayed in cell C5. The number is less than 1.
- Next, select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to replicate the formula for the rest of the cells.
- While cell C5 is selected go to the Home tab.
- Then go to the Editing group and click Sort & Filter.
- Now select Sort Smallest to Largest from the drop-down menu.
- As soon as you click the command, your rows will randomize themselves. It is noticeable that not only column C, but all the columns have also been randomly changed along the rows.
So these are the steps you can follow when you got a dataset with multiple columns and you want to randomize your rows in such a way that all the columns along a row randomize their values.
12. Extract File Name from URL
Sometimes you may have a list of URLs and you need to extract only the file name. In the following way, you can extract the file name from a URL. Assume cell B5 contains this example URL: “http://example.com/assets/images/horse.jpg”. If you want you can use any real URL of your need.
We are gonna need a formula consisting of a whole plethora of functions here. Don’t worry, there is an explanation added later to understand how it works. This formula contains RIGHT, LEN, FIND and SUBSTITUTE functions in it.
Now follow these steps to extract the file name (horse.jpg) from the link.
Steps:
- First, select the cell where you want to put the file name. In this case, it is cell C5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=RIGHT(B5,LEN(B5)-FIND("*",SUBSTITUTE(B5,"/","*",LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,"/","")))))
- After that, press Enter.
🔎 Breakdown of the Formula
👉 SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””) removes all the “/” from the URL. It returns http:www.example.comassetsimageshorse.jpg.
👉 LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””)) returns the length of the previous string.
👉 LEN(B5) returns the length of the string in cell B4 which is 46 here.
👉 LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””))) indicates the difference between the two length values. This in turn indicates the number of “/” were removed.
👉 SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,”*”,LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””))) substitutes all the slashes (/) is cell B5 with star sign (*) with the instance number from the result of the previous function.
👉 FIND(“*”,SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,”*”,LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””)))) finds the position “*” is in the string up until now.
👉 LEN(B5)-FIND(“*”,SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,”*”,LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””)))) is the difference between the original string length and the previous position.
👉 Finally, RIGHT(B5,LEN(B5)-FIND(“*”,SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,”*”,LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5,”/”,””))))) extracts that number of characters from the right side of the cell.
13. Match Text in List
Let’s take a look at the following figure. We are going to find out the persons who have resigned from the left side of our example. There is a list on the right side of the resigned numbers.
The above one shows a simple example. The data is in the range B5:D133. The goal is to identify the rows in the data zone which are appearing in the Resigned Members list, in column G. You can delete these unnecessary rows later. We are going to need a combination of the IF and COUNTIF functions for the purpose.
Follow these steps to see how we can achieve the resigned status in our dataset.
Steps:
- First, select cell E5.
- Then write down the following formula.
=IF(COUNTIF($G$5:$G$25,C5),"Resigned","")
- After that, press Enter.
- Now double-click the fill handle icon on the bottom-right corner of the cell border. You can also click and drag. But as the dataset is large, we are opting for the previous method.
- Once you have done that, the spreadsheet will look like this.
This is how we can match text as part of the data analysis techniques in Excel.
Read More: How to Remove Partial Data from Multiple Cells in Excel
14. Change Vertical Data to Horizontal
Transposing or changing vertical to horizontal and vice versa in a dataset is another common one in data analysis. So we will be discussing changing vertical data to horizontal now in the series of data cleaning techniques in Excel.
For that, we will be using the following dataset.
Using Paste Special Option
The easiest way to change a vertical column to a horizontal row is to use the Paste Special option of Excel. It also keeps the exact formatting while changing the vertical column. So, you don’t need to apply any formatting later. Let’s follow the steps below to see how we can use the Paste Special option to transpose the columns.
- First of all, select the range that you want to change to horizontal rows. Here, we have selected the range B4:C10.
- Secondly, press Ctrl+C to copy the range.
- Thirdly, select a cell where you want to paste the range horizontally. In our case, we have selected Cell B12.
This will change vertical columns into horizontal rows in the Excel spreadsheet.
Using TRANSPOSE Function:
We can use some Excel Functions to convert a vertical column to a horizontal row. Here, we will use the TRANSPOSE function for that purpose. The main advantage of using functions is that you will get dynamic updates in the horizontal rows if you change anything in the main dataset. But, the horizontal rows will not have the same formatting as the vertical columns. You need to add formatting after applying the method.
Let’s follow the steps below to learn more.
Steps:
- First, select the cell where you want to place the formula.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=TRANSPOSE(B4:C10)
- Now press Enter.
This is how we can change vertical data to horizontal using the TRANSPOSE function.
15. Fill Blank Cells
One of the most important data cleaning techniques in any form of data analysis is filling blank values, either with average in numeric cases or with values with the previous or later rows.
Sometimes we keep some blank cells to understand that they will be the first filled ones, have a look at our dataset to understand it. But sometimes it creates problems like while we are filtering or sorting data. So it’s better to fill them and there are easy ways to do it.
This is our dataset.
We can fill them up using these two simple methods.
Using Fill Command
If your data is small, you can enter the missing cell values from above manually or by using this command. Follow these steps to see how you can do that.
- Select Cell B6.
- Then go to the Home
- From the Editing group, click on Fill and then Down.
- The dataset will look like this now.
- Now repeat the process for all the blank cells and fill out all the cells.
This is one way to fill up blank cells in a dataset.
Using Keyboard Shortcut:
We can achieve the same result using a keyboard shortcut. The shortcut is Ctrl+D. You just have to select the blank cell and press the shortcut. It will fill the cell with the value from the previous cell in the same column. Follow these steps for a more detailed guide.
- First, select cell B6.
- Then press Ctrl+D on your keyboard.
- Now selecting cell B9 and pressing Ctrl+D will yield the following result.
- Now fill out all the blank values by selecting them and pressing the shortcut.
16. Check Spelling
When you use Microsoft Word Document or another word processor, you use its spell checker feature most of the time. Spelling mistakes in a text document are embarrassing. In Excel, spelling mistakes can also occur serious problems. Say, for example, if you tabulate data by month, a misspelled month name will make that a year has 13 months.
Here we have made a dataset for the demonstration.
We are going to correct the range C5:C7. Follow these steps to see how we can do that.
Steps:
- First, select the range C5:C7.
- Then go to the Review tab and select Spelling from the Proofing You can also skip this step and press F7 on your keyboard.
- Now select the correct suggestion and click on Change to change the value of a particular cell. The errors come in the selection order here.
- This will change the first error in the dataset.
- Now repeat this process for all the errors and you will have correct spellings this way.
17. Replace or Remove Text
Removing and replacing data, especially outliers is another important task in any data cleaning process. So as a part of our data cleaning techniques compilation, we are going to demonstrate replacing and removing text in Excel. We can do that using three methods.
For all of the methods, we are using the following dataset.
Using Find & Replace Feature:
Excel has a direct feature that can help find, replace and remove certain values from another. Follow these steps to see how we can use this feature to remove or replace in Excel.
- First, select the range which you want to modify. In this case, it is C5:C13.
- Then go to the Home
- After that, select Find & Replace from the Editing group section.
- Next, select Replace from the drop-down.
- Now, go to the Replace tab in the pop-up box.
- Then insert the value you want to replace in the Find what field and the value you want to replace it with in the Replace with
- Finally, click Replace All to replace all of them in the dataset.
This will be the final product after removing all of the hyphens from the dataset.
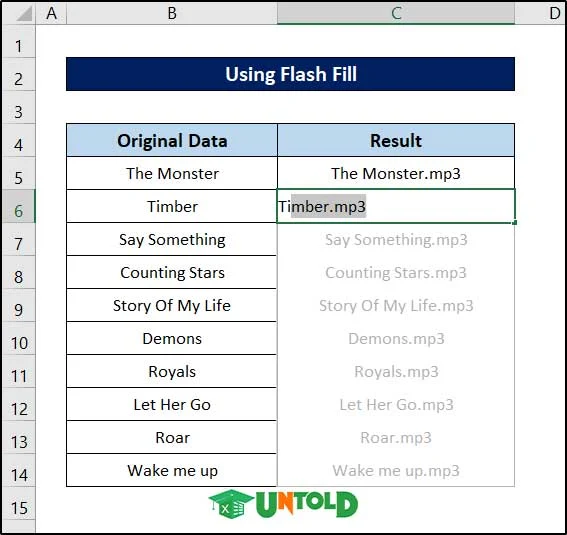
Utilizing Flash Fill:
Another feature we can use to replace or remove values while using data cleaning techniques is to utilize the flash fill feature. For the same dataset, follow these steps to see how that works.
- First, write down the final product after removing or replacing the desired value in the first cell. We are replacing the second hyphen in the string with a colon.
- Now start writing the second one manually. As soon as you start writing Excel will recognize the pattern and start suggesting output for the rest.
Note
If the suggestion doesn’t occur in the second entry, try it out manually. It sometimes suggests the output at the third or fourth entry if the pattern isn’t that obvious to Excel.
- Now press Enter.
Thus, you can replace or remove values using this handy feature of Excel while data cleaning.
Using SUBSTITUTE Function:
Another way we can replace a value, or remove them in Excel is to use the SUBSTITUTE function. This function takes three values- a string, the value to replace, and the value to replace it with. Follow these steps to see how we can use this function.
- First, select cell C5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=SUBSTITUTE(B5,"-",":",2)
- After that, press Enter.
- Finally, select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to replicate the formula for the rest of the cells.
Read More: Using Excel to Clean and Prepare Data for Analysis
18. Add Text to Cells
Adding text is not only common as one of the data cleaning techniques but also in general Excel operations. We can add text to cells in various ways. For demonstrations of those, we will use the following dataset.
Now you can use one of the following methods to add text to cells.
Using Ampersand (&) Symbol:
The ampersand (&) symbol in a formula works as the string connector. It connects the previous and the following string it is in between. Follow these steps to see how we can easily add text to cells using this.
- First of all, select cell C5.
- Secondly, put down the formula below.
=B5&".mp3"
- Next, press Enter.
- Finally, click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to replicate the formula for the rest of the cells.
Applying Flash Fill Feature:
Follow these steps to add text using the flash fill feature easily in Excel.
- First, write down the first intended value manually in cell C5.
- Then start filling out the second one in the dataset. Once you start filling, Excel will suggest the pattern.
- As soon as the suggestion appears, press Enter.
This is another way to add text in Excel.
Using CONCATENATE Function:
The CONCATENATE function in Excel, as the name suggests, concatenates two or more strings together. It takes those strings as its arguments. It works the same way as the ampersand sign method described earlier. Follow these steps to see how we can use this function.
- First, select cell C5.
- Then write down the following formula in it.
=CONCATENATE(B5,".mp3")
- After that, press Enter.
- Finally, select the cell again and click and drag the fill handle icon to the end of the column to replicate the formula for the rest of the cells.
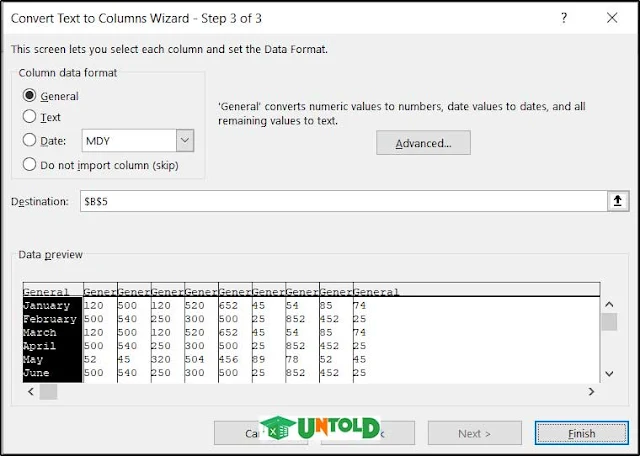
19. Fix Trailing Minus Sign
Sometimes while taking data from other sources, the negative values do have a trailing minus sign. Take a look at the following figure.
Excel doesn’t consider the values with trailing negative signs as numbers. Instead, it treats them as texts. This may cause problems, not only in the data cleaning techniques but also in general operations like using formulas in Excel. So we need to address the problem and convert them into negative numbers.
Follow these simple steps to do that.
Steps:
- First, select the range you want to convert. We have copied it to compare it with the previous one.
- Then go to the Data tab on your ribbon.
- Then select Text to Columns from the Data Tools group section.
- Finally, directly click on Finish in the wizard.
This will automatically change all the negative values with trailing minus signs to Excel’s negative sign format.
This procedure works because there is a default setting in the Advanced Text Import Settings dialog box.
Conclusion
So these were some of the most useful data cleaning techniques in Excel used for data analysis. Hopefully, you can use these techniques while using data cleaning in Excel with ease. I hope you found this guide helpful and informative. If you have any questions or suggestions, let us know in the comments below.




































































































No comments:
Post a Comment